How to Choose the Right Tubing and Fittings: A Guide to Materials, Sizes, and Pressures
 2025.09.22
2025.09.22
 Industry news
Industry news
In modern industry and machinery, air hoses and fittings are essential components of pneumatic systems. They not only deliver compressed air but also directly affect system performance and safety. If chosen improperly, efficiency may drop, equipment may fail, and safety risks may arise.
Material Selection for Air Hoses and Fittings
The material of hoses and fittings determines their durability, flexibility, pressure resistance, and suitability for different environments. Each material has unique advantages, limitations, and applications.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Advantages:
- Low cost, very economical
- Lightweight, easy to handle and install
- Flexible, easy to bend and route
Disadvantages:
- Low pressure resistance, unsuitable for high-pressure systems
- Poor abrasion resistance, wears out faster in friction-heavy environments
- Weak heat resistance, unsuitable for high-temperature applications
Applications:
PVC hoses are best suited for light pneumatic tools, short-distance air delivery, and laboratory or low-pressure systems. Their low cost makes them ideal for temporary or mobile applications.
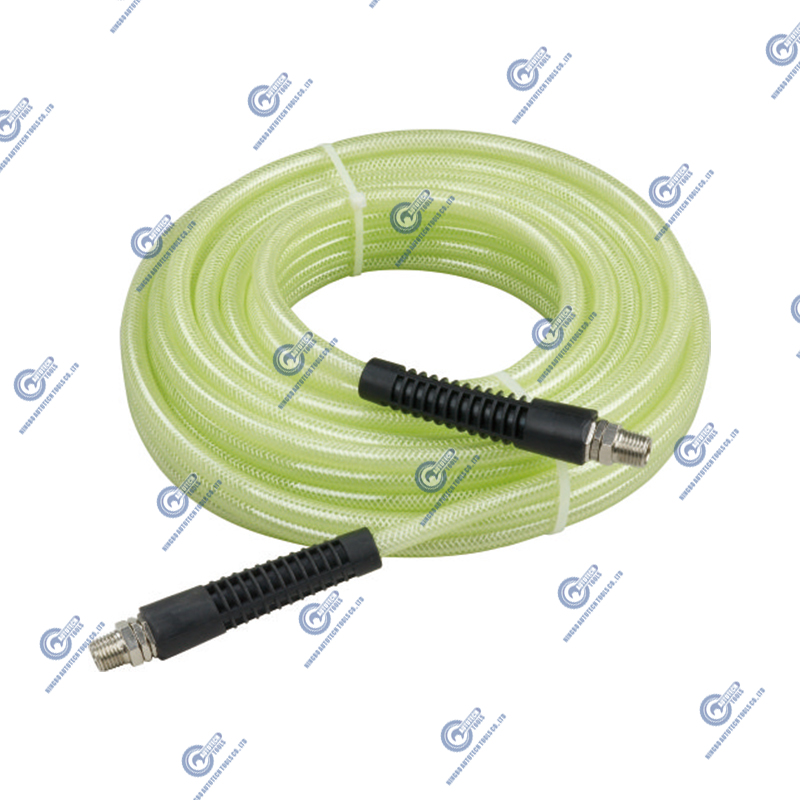

PU (Polyurethane)
Advantages:
- Excellent flexibility, resists kinking
- High abrasion resistance, ideal for frequent movement
- Good low-temperature performance, can be used in cold environments
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to PVC
- Performance may be affected at very high temperatures
Applications:
PU hoses are widely used in automotive repair, factory assembly lines, and pneumatic tools requiring frequent movement. Their durability and flexibility make them popular in industrial settings.
Rubber
Advantages:
- High pressure resistance, suitable for heavy-duty systems
- Aging resistance, long service life
- Good heat resistance, suitable for high-temperature applications
Disadvantages:
- Heavier than PVC and PU hoses
- Opaque, making it hard to visually monitor airflow
Applications:
Rubber hoses are ideal for high-pressure pneumatic systems, heavy industry, and environments requiring long-lasting durability.
Nylon
Advantages:
- Strong corrosion resistance, suitable for harsh environments
- Lightweight, easy to route
- Good rigidity, maintains shape well
Disadvantages:
- Limited flexibility, not suitable for frequent bending
- Over-bending may lead to cracking
Applications:
Nylon hoses are commonly used in chemical, food, and other industries requiring corrosion resistance and high cleanliness.
Fitting Material Selection
The material of fittings must match the hose to ensure durability and proper sealing. Common materials include:
| Material | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Brass | Corrosion-resistant, easy to machine | General industrial use |
| Stainless Steel | High strength, corrosion-resistant | High-pressure, high-temperature, chemical environments |
| Nickel-plated Steel | Durable and economical | Medium- to low-pressure systems |
Size Selection for Air Hoses and Fittings
The size of hoses and fittings directly impacts airflow, pressure loss, and usability.
Inner Diameter (ID)
Importance:
- Larger ID = higher airflow
- Too small ID = insufficient supply for pneumatic tools
Recommendation:
Choose based on tool demand. Common sizes include 4mm, 6mm, 8mm, and 10mm. For high-flow systems, use larger diameters.
Outer Diameter (OD)
Importance:
- Determines compatibility with fittings
- Mismatched OD may cause leaks or installation issues
Recommendation:
Ensure the hose OD matches the fitting specification for proper sealing.
Hose Length
Impact:
- Excessive length increases pressure loss
- Too short limits mobility and usability
Recommendation:
Select a length that fits the workspace with some allowance, avoiding overstretching or frequent disconnection.
Pressure Rating Selection
Pressure ratings determine the safety and durability of hoses and fittings.
Working Pressure
Definition: The maximum pressure the hose can withstand continuously.
Recommendation: Choose a hose with a working pressure higher than system operating pressure.
Burst Pressure
Definition: The maximum pressure a hose can withstand under extreme conditions.
Rule of Thumb: Usually 3–4 times the working pressure.
Safety Factor
Always choose hoses and fittings with a margin above system pressure to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and maintenance extend service life and improve system safety.
Installation Tips
- Install fittings correctly, avoiding over-tightening or misalignment
- Use sealing tape or compound to ensure airtight connections
Regular Inspection
- Check for wear and cracks, replace damaged hoses promptly
- Avoid excessive bending or flattening, which reduces airflow
Environmental Protection
- Keep hoses away from high heat, sharp objects, and corrosive chemicals
- Store coiled hoses properly, avoid sharp bends, and maintain flexibility















