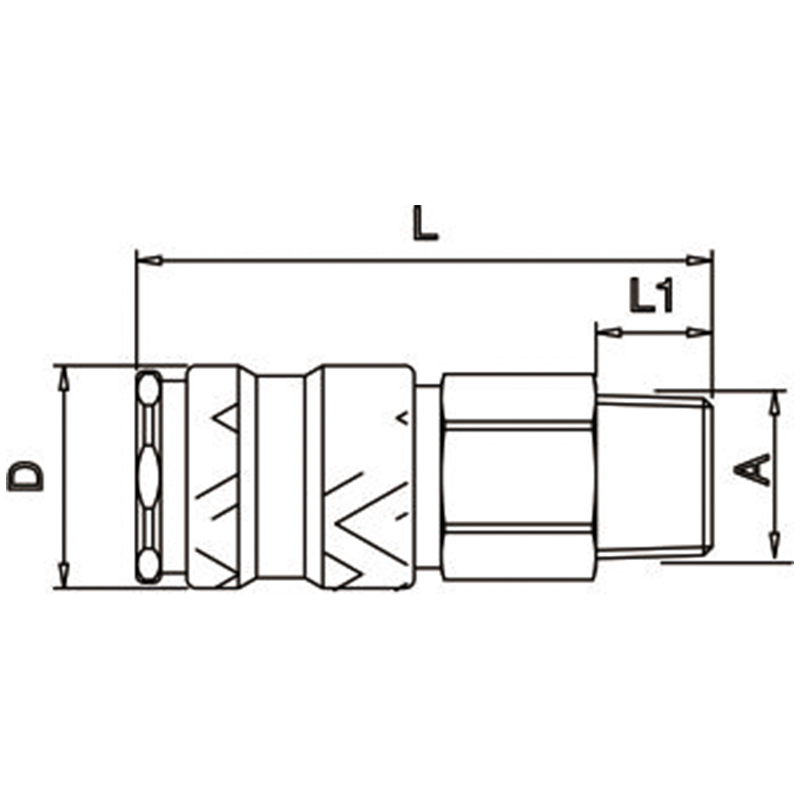
| Push To Connect, Male Pipe Thread | |||||
| CODE | SIZE | L | D | L1 | SW |
| E25K-2SM | 1/4" | 59.5 | 23 | 10 | 19 |
| E25K-3SM | 3/8" | 57.5 | 23 | 9 | 19 |
| E25K-4SM | 1/2" | 60.5 | 23 | 12 | 24 |
Material:
Universal industrial coupling with standard European profile for use with gaseous, liquid and aggressive media.
Coupling system with single-hand operation. High Flow valve for optimum flow and low pressure drop.
The series stands out for its robust design and long service life even with the harshest use.
The collar design minimizes damage to the valve body.
Interchangeable industrial profile couplings for compressed air are designed for ISO 6150B standards
High flowrate valve for best flow performance and low pressure drop
Steel sleeve neutralizes vibrating forces
Single-hand operation
Operating Temperature:-20°C to +100°C
Operating Pressure: 0-35 bar
Interchangeability: Rectus 23K / Milton M-Style / Amflo Type C

Detailed parameters

| Push To Connect, Male Pipe Thread | |||||
| CODE | SIZE | L | D | L1 | SW |
| E25K-2SM | 1/4" | 59.5 | 23 | 10 | 19 |
| E25K-3SM | 3/8" | 57.5 | 23 | 9 | 19 |
| E25K-4SM | 1/2" | 60.5 | 23 | 12 | 24 |
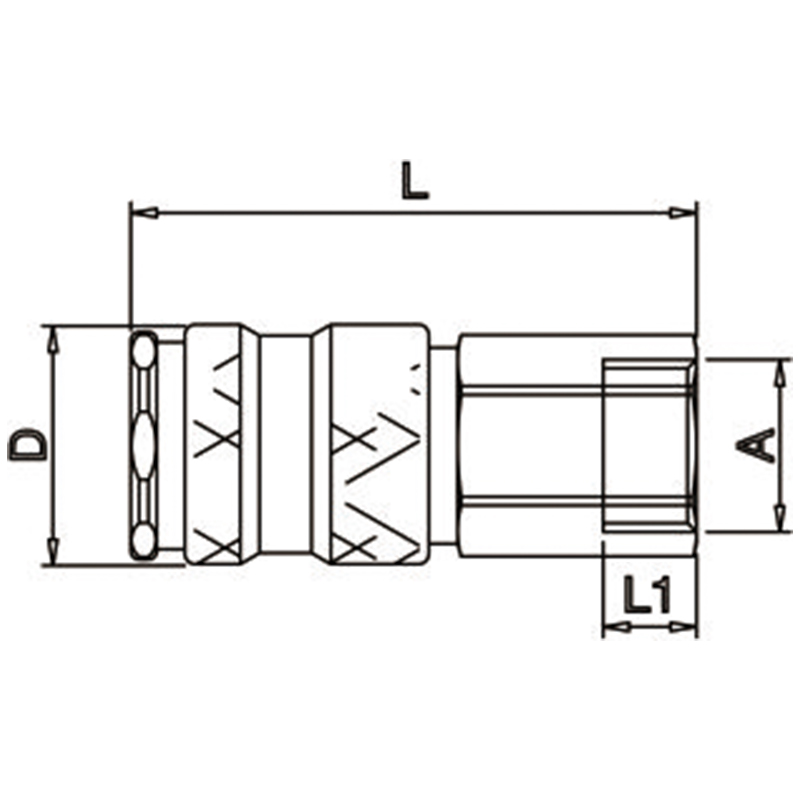
| Push To Connect, Female Pipe Thread | |||||
| CODE | SIZE | L | D | L1 | SW |
| E25K-2SF | 1/4" | 55.5 | 23 | 10 | 19 |
| E25K-3SF | 3/8" | 54.5 | 23 | 9 | 19 |
| E25K-4SF | 1/2" | 57.5 | 23 | 12 | 24 |
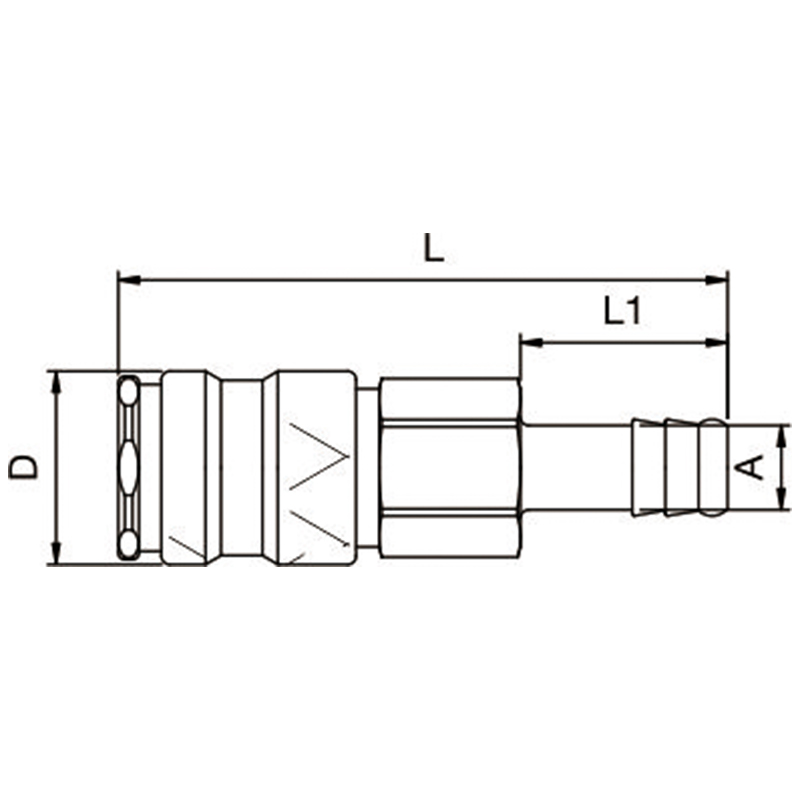
| Push To Connect, Standard Hose Barb | |||||
| CODE | SIZE | L | D | L1 | SW |
| E25K-2SH | 6MM | 73.5 | 23 | 25 | 19 |
| E25K-3SH | 8MM | 73.5 | 23 | 25 | 19 |
| E25K-4SH | 10MM | 73.5 | 23 | 25 | 19 |
KEEP IN TOUCH

When you’re maintaining your vehicle, ensuring that your tires are inflated to the correct pressure is a vital aspect of both safety and performance. A Tire Gauge & Inflator is a must-ha...
READ MOREAir hoses and fittings are fundamental components in any pneumatic system. They serve as the pathway for compressed air to reach tools, machinery, or industrial equipment. Selecting the righ...
READ MOREInstalling couplers and plugs requires careful attention to safety, as improper handling can lead to serious hazards like electrical shocks, equipment damage, or even fire. These components ...
READ MORE