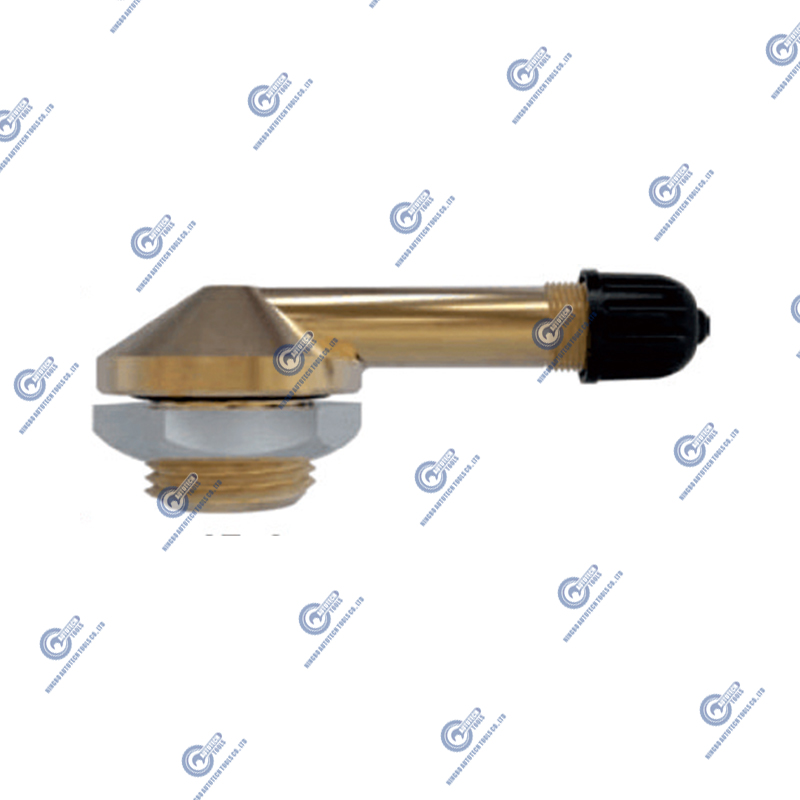
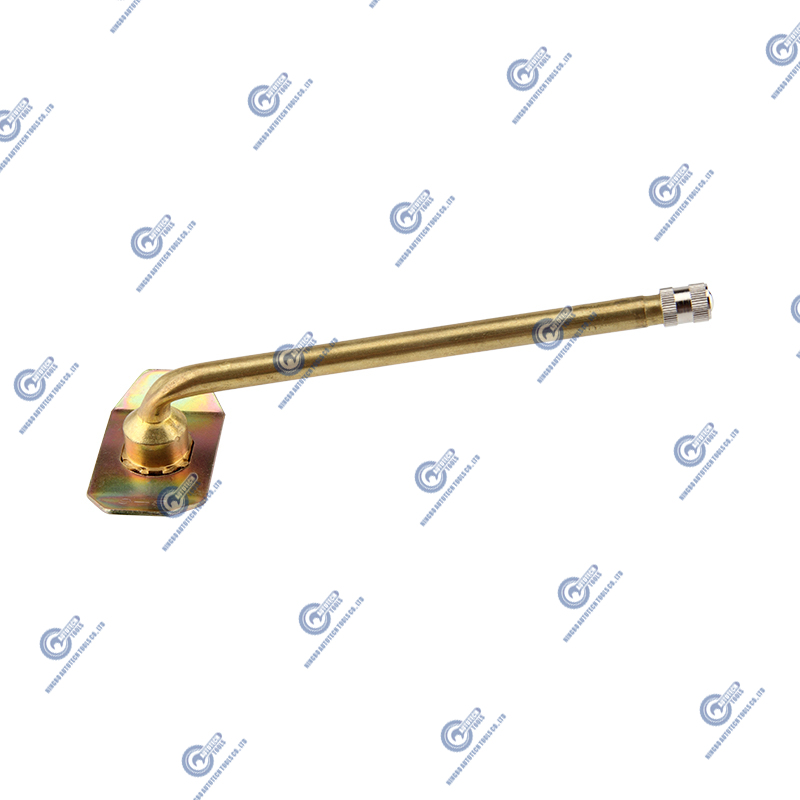
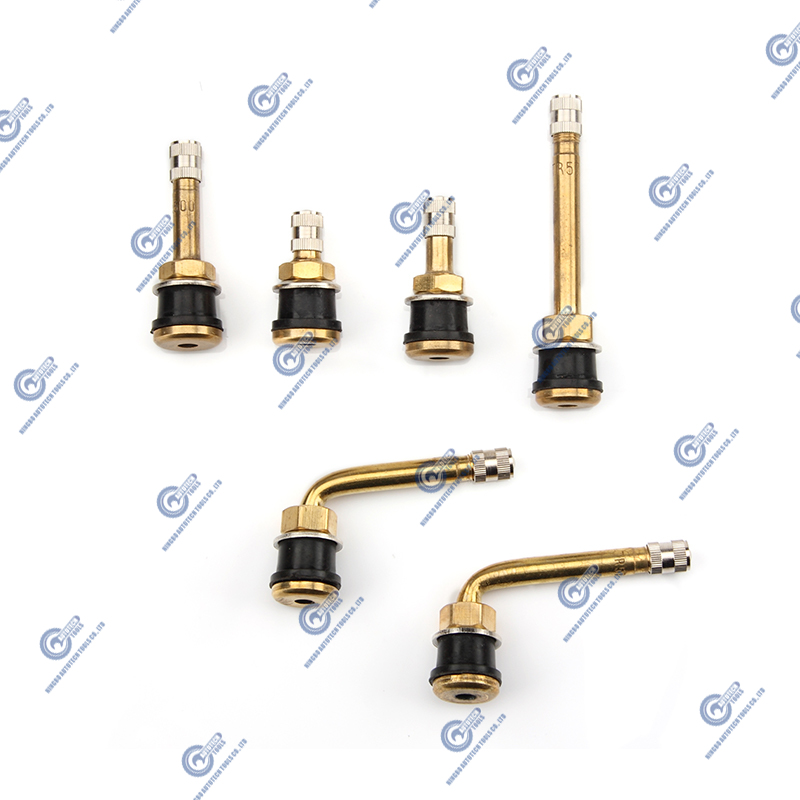
What are rubber base valves? What is their role in the industry?
 2026.01.05
2026.01.05
 Industry news
Industry news
Rubber base valves are a type of valve that incorporates rubber components in its structure. The key function of a rubber base valve is to ensure a tight seal in fluid or gas systems, primarily through the use of rubber sealing elements. These valves are designed to regulate the flow of fluids or gases while preventing leakage, making them essential in various industries that require reliable sealing and flow control.
The core components of these valves typically include rubber gaskets, rubber valve seats, or other rubber sealing parts that provide a durable and effective sealing mechanism. Rubber base valves find applications in many industries, such as industrial manufacturing, water treatment, chemical processing, and even in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
Main Features and Advantages of Rubber Base Valves
- Flexibility: The use of rubber material allows these valves to withstand small movements or vibrations within piping systems without compromising their sealing ability. This is particularly important in applications where vibration or thermal expansion occurs.
- Excellent Sealing Properties: Rubber provides a tight seal, preventing leaks of gases and liquids. In high-pressure, high-temperature, or chemically corrosive environments, rubber base valves maintain a high level of sealing efficiency over time.
- Durability: Rubber base valves are highly resistant to corrosion and wear. This makes them suitable for long-term use in harsh conditions, such as chemical plants or water treatment systems, where they can operate effectively for extended periods.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to metal valves, rubber base valves are relatively inexpensive to manufacture. This makes them an affordable option for large-scale applications where many valves are needed, reducing overall maintenance costs.
Applications of Rubber Base Valves Across Various Industries
Rubber base valves are widely used across multiple industries, with the following being some of the most common application areas:
| Application Area | Detailed Explanation |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing | In manufacturing processes, rubber base valves are used to control the flow of liquids or gases, ensuring precise fluid supply on production lines. |
| Water Treatment | In water treatment systems, rubber base valves are ideal for regulating flow and preventing water leaks due to their sealing performance and corrosion resistance. |
| Automotive | Rubber base valves are used in engine cooling systems, fuel systems, and air intake systems in the automotive sector, providing strong sealing and high-temperature resistance. |
| HVAC Systems | In HVAC systems, rubber base valves regulate airflow and pressure to ensure efficient operation and reduce energy consumption. |
| Chemical Processing | In chemical plants, the chemical resistance of rubber base valves makes them suitable for handling corrosive liquids and gases, preventing leaks and maintaining process safety. |
Adaptability of Rubber Base Valves in Various Environments
Rubber base valves are capable of adapting to a wide range of environmental conditions, especially in high-pressure, high-temperature, and corrosive settings. For example, in chemical processing and water treatment industries, rubber base valves can effectively resist strong acids and alkalis, ensuring long-term stable performance. Moreover, the versatility of rubber materials allows the valves to perform efficiently under varying temperatures, humidity, and climate conditions.
In systems that require pressure control of liquids and gases, rubber base valves can handle the fluctuations in pressure without compromising their sealing ability. The durability of rubber ensures that these valves remain effective even after long periods of use, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
FAQ
Q1: How long do rubber base valves last?
A1: The lifespan of a rubber base valve depends on its operating environment, material quality, and maintenance practices. Generally, under normal operating conditions, rubber base valves can last anywhere from 5 to 10 years. In harsh environments, such as high temperatures or chemically corrosive conditions, their lifespan may be shorter.
Q2: How do you maintain rubber base valves?
A2: Maintenance of rubber base valves primarily involves regularly checking the sealing performance, cleaning the rubber surfaces, and inspecting for any wear or aging signs. Regular inspections are particularly important in high-pressure and high-temperature environments to ensure that the valve continues to function effectively.
Q3: Are rubber base valves suitable for all types of fluids?
A3: Rubber base valves are widely used for controlling both liquid and gas flow. However, different types of rubber materials are suited for different types of fluids. For example, rubber with chemical resistance is ideal for handling strong acids or alkalis. It is essential to select the appropriate rubber material based on the specific fluid being handled.
Q4: Are rubber base valves better than metal valves?
A4: Rubber base valves and metal valves each have their own advantages. Rubber base valves are more cost-effective, offer better sealing properties, and provide more flexibility, making them suitable for medium- to low-pressure applications. Metal valves, on the other hand, are better suited for high-pressure, high-temperature, and more complex fluid control systems. The choice between the two depends on the specific application requirements.
References
- Smith, J. (2020). The Role of Rubber Seals in Fluid and Gas Flow Control. Industrial Valve Journal, 14(3), 56-62.
- Li, X., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Advancements in Rubber-Based Valve Technology for Harsh Environments. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 42(7), 789-794.
- Patel, R. (2018). Sealing Systems in Hydraulic and Pneumatic Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Valve Systems International, 22(2), 101-115.















